E-Commerce SEO Checklist: 13 Steps to Higher Rankings

Last Updated on 12 January 2026 by Dorian Menard
As the founder of Search Scope, a Perth-based SEO consultancy offering E-commerce SEO services, I’ve seen firsthand what separates a struggling online store from a thriving one.
This comprehensive e-commerce SEO checklist is designed for Australian business owners who want to increase their rankings, attract qualified traffic, and generate more sales. We’ll skip the fluff and focus on the practical steps that deliver measurable results, moving from foundational setup to advanced strategies for 2025.
Here’s the fastest path to better rankings:
- Nail the Foundations: Set up essential tools and technical files correctly from day one.
- Optimise Core Pages: Focus on making your product and category pages workhorses for both users and search engines.
- Improve Site Performance: Master Core Web Vitals to provide a fast, seamless user experience that Google rewards.
- Build Authority: Use content marketing, user reviews, and digital PR to build trust and attract high-quality links.
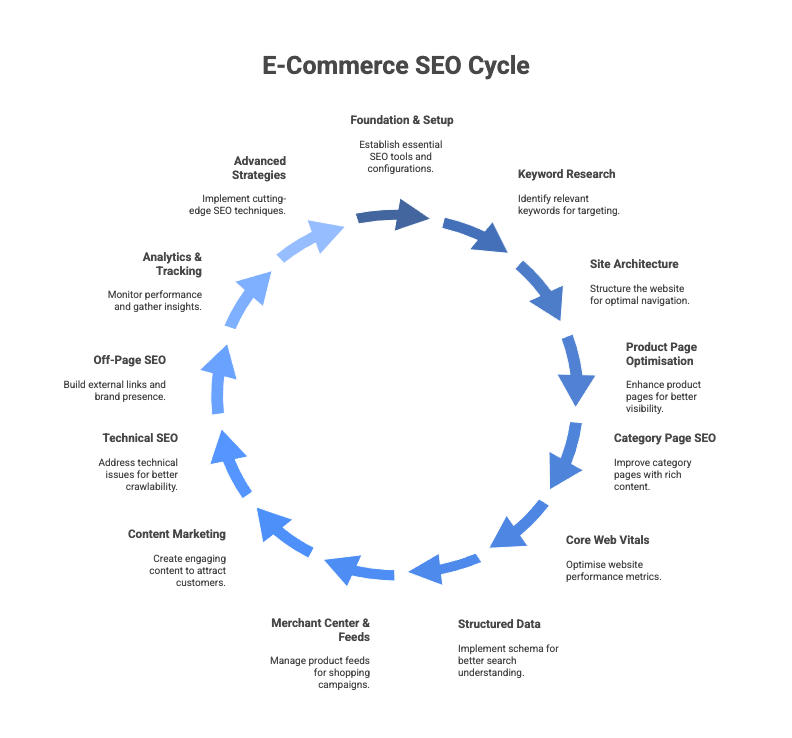
1. Getting Your Technical Foundations Right
To run an effective SEO campaign and generate quality traffic, a few fundamentals are non-negotiable. Getting these right prevents major headaches later.
What are the essential tools for e-commerce SEO?
Google Search Console
This is your direct line of communication with Google. It’s completely free and provides critical data on your site’s health and performance.
- Verify your domain ownership to get started.
- Submit your XML sitemaps so Google can find all your pages.
- Monitor Core Web Vitals alerts for performance issues.
- Track keyword performance and click-through rates (CTR).
Google Analytics 4
GA4 is how you understand what users do after they land on your site. It helps you track sales, user behaviour, and the overall return on your SEO investment.
- Enable enhanced e-commerce tracking to see detailed purchase activity.
- Set up conversion goals for actions like “add to cart” or newsletter sign-ups.
- Configure audience segments to analyse different customer groups.
- Integrate heatmap tools like Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity to visualise user clicks and scrolls.
Google Merchant Center
This is essential for getting your products to appear in Google Shopping results. A well-maintained feed is the key to visibility.
- Create and submit a product feed with accurate, up-to-date information.
- Verify your business information to build trust.
- Link to your Google Ads account for Shopping campaigns.
- Check your feed health in the “Diagnostics” tab at least weekly to fix errors.
Example feed attributes for a clothing store:
id: SKU12345
title: Men's Blue Cotton T-Shirt - Medium
description: Comfortable 100% cotton t-shirt perfect for casual wear
link: https://example.com.au/mens-blue-cotton-tshirt
image_link: https://example.com.au/images/blue-tshirt-main.jpg
availability: in stock
price: 24.99 AUD
brand: YourBrand
condition: new
google_product_category: Apparel & Accessories > Clothing > Shirts & Tops
product_type: Men > T-Shirts > CasualHow do you establish core SEO settings?
Install an SSL Certificate
HTTPS is a confirmed Google ranking factor and is absolutely essential for customer trust. Modern browsers flag non-HTTPS sites as “Not Secure,” which can kill conversions. While free options like Let’s Encrypt exist, I often advise clients to invest in a premium SSL certificate from providers like DigiCert for the added trust signals and warranty.
Set Up Your Robots.txt File
This simple text file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Use it to block access to admin areas, customer carts, and internal search result pages to conserve your crawl budget for important URLs.
Example e-commerce robots.txt:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
# Block admin and customer areas
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /account/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /orders/
# Block search and filter parameters
Disallow: /*?sort=
Disallow: /*?filter=
Disallow: /*?price=
Disallow: /*?color=
# Block duplicate session URLs
Disallow: /*?sid=
Disallow: /*?sessionid=
# Block thank you and confirmation pages
Disallow: /thank-you/
Disallow: /order-confirmation/
# Allow important files
Allow: /sitemap.xml
Allow: /robots.txt
# Sitemap location
Sitemap: https://yourstore.com.au/sitemap.xml
Create XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a roadmap of your website for search engines. For e-commerce stores, it’s best to generate separate sitemaps to keep things organised and help Google prioritise crawling.
- Pages: Your homepage, category pages, and other key static pages.
- Products: All individual product pages, with higher priority weighting for bestsellers.
- Images: Include all product images with descriptive metadata.
- Videos: If you use product videos, a dedicated sitemap helps them get indexed.
- Blog: All your articles and guides, if applicable.
2. Keyword Research & Strategy
Effective keyword research is about understanding customer intent. You need to know what your audience is searching for at every stage of their buying journey.
Analyse Search Intent with the Right Tools
Use Advanced Keyword Research Tools
Free tools are a starting point, but professional tools provide the competitive edge you need. They reveal what your competitors rank for and what questions your customers are asking.
| Tool | Key Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Google Keyword Planner | Free, direct Google data | Initial brainstorming and CPC data |
| SEMrush | Excellent competitor analysis | Finding keyword gaps and tracking rankings |
| Ahrefs | Superior backlink data | Content cluster planning and link building |
How should you map keywords by intent?
Matching keywords to the right page type is fundamental. This ensures you’re meeting the user’s needs at the exact moment they search.
- Informational Intent: “how to choose a wetsuit” → Target with a detailed blog post or buying guide.
- Commercial Intent: “best 3/2mm wetsuits” → Target with a well-optimised category page.
- Transactional Intent: “buy O’Neill Hyperfreak 3/2mm medium” → Target with a specific product page.
Develop a Smart Long-Tail Keyword Strategy
Why long-tail keywords are perfect for e-commerce
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that shoppers use when they’re closer to making a purchase. According to research from Ahrefs, long-tail keywords with more than three words make up the vast majority of all searches. They have lower competition and much higher conversion rates.
| Keyword Type | Example | Monthly Searches | Competition | Conversion Intent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad | “hiking boots” | 30,000 | High | Low |
| Medium-tail | “men’s hiking boots” | 5,000 | Medium | Medium |
| Long-tail | “waterproof hiking boots for men size 11” | 120 | Low | High |
| Ultra-long | “best lightweight waterproof hiking boots for wide feet” | 40 | Very Low | Very High |
Where can you find customer language to target?
The best keywords come directly from your customers. You can uncover a goldmine of long-tail terms by listening to how they talk about your products.
- Analyse your own site’s search logs to see the exact queries people use.
- Review product page Q&As and customer service chat logs.
- Use tools like AlsoAsked.com to find “People Also Ask” questions at scale.
- Browse Reddit threads and online forums related to your products.
3. Site Architecture & Navigation
A logical site structure helps both users and search engines find what they’re looking for. It’s the blueprint of your online store.
Optimise Your Information Architecture
Build an Intuitive Site Structure
A clear structure improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and helps spread link authority throughout your site. The golden rule is to keep every product within three clicks of the homepage.
How do you create strategic categories?
Your main navigation should be simple and intuitive. Use language your customers would use, not internal jargon.
- Group products by how customers shop (e.g., “Shop by Activity” or “Shop by Brand”).
- Limit your main navigation categories to 5-7 items to avoid overwhelming users.
- Create clear subcategory hierarchies that flow logically from broad to specific.
Category pages are powerful ranking assets that are often under-optimised. They allow you to rank for broader terms and funnel authority down to your product pages.
Add Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs are secondary navigation aids that show users their location on your site. They also help search engines understand your site’s hierarchy and can appear in search results, which improves visibility. Be sure to implement BreadcrumbList schema markup.
How to handle faceted navigation vs. URL structure?
Control Faceted Navigation SEO
Faceted navigation (product filtering) is great for users but can create thousands of duplicate, low-value URLs. For example, on a Shopify store, an app like Product Filter & Search can create many parameter-based URLs that need to be managed carefully.
- Use canonical tags to point filtered URLs back to the main category page.
- Use the
noindextag on filter combinations that don’t have significant search demand. - Create static, indexable pages for valuable filter combinations (e.g., “/mens-shoes/trail-running/”).
- Configure parameter handling rules in Google Search Console to tell Google how to treat your URLs.
Optimise Your URL Structure
Clean, descriptive URLs are better for both users and SEO. They should be easy to read and give a clear indication of the page’s content.
- Keep URLs short, descriptive, and readable.
- Include your primary keyword where it makes sense.
- Use hyphens (-) to separate words, not underscores (_).
Good URL example:
/clothing/mens/jackets/waterproof-jackets/brand-x-goretex-jacket-black
Poor URL example:
/cat.php?id=42&sub_id=11&prod=9987
4. Product Page Optimisation
Your product pages are where conversions happen. Each page needs to be perfectly optimised to convince both search engines and customers.
Create Compelling On-Page Content
Write Unique Product Descriptions
Never use generic manufacturer descriptions. They are often thin on detail and create duplicate content issues across multiple retail sites. Instead, write original copy that focuses on benefits, not just features.
If you have thousands of products, this can seem daunting. However, AI writing assistants like Jasper or Copy.ai can help you scale the process by creating unique drafts based on your product attributes, which you can then edit and refine.
Optimise Product Titles & Meta Tags
Your titles and descriptions are your sales pitch in the search results. Make them clear, compelling, and click-worthy.
| Element | Best Practice | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Title Tag | Product Name | Category | Brand Name | “XPS 15 Laptop | Laptops | Dell Australia” |
| H1 Heading | Clear product name with primary keyword | “Dell XPS 15 Laptop with OLED Display” |
| Meta Description | Summarise key benefits, features, and include a call-to-action (CTA). | “Experience the powerful Dell XPS 15 Laptop. Featuring a stunning 4K OLED display and Intel Core i9 processor. Free shipping Australia-wide. Buy now.” |
What kind of media should you use on product pages?
Optimise Product Images
High-quality images are critical for e-commerce. They must also be optimised for search and performance.
- Use descriptive filenames like `dell-xps-15-laptop-side-view.jpg`.
- Write detailed alt text: “Side view of the Dell XPS 15 laptop showing USB-C and SD card ports”.
- Compress images and serve them in next-gen formats like WebP or AVIF.
- Include multiple angles, close-ups, and lifestyle shots of the product in use.
Add Product Videos
Product videos can significantly lift conversion rates. A Wyzowl report found that 88% of people were convinced to buy a product after watching a brand’s video.
Create short demonstration videos, 360-degree views, or tutorials. Host them on platforms like YouTube or Vimeo and embed them on your product pages with VideoObject schema markup to get a video thumbnail in search results.
Build Trust with User-Generated Content
Implement Customer Review Systems
Reviews are a powerful form of social proof and a key ranking factor. Use platforms like Yotpo or Trustpilot to automate review collection and display.
- Enable star ratings and use AggregateRating schema to get rich snippets in search results.
- Encourage customers to leave detailed written reviews with post-purchase emails.
- Always respond to reviews, both positive and negative.
Add Product Q&A Sections
A Q&A section lets potential customers ask questions and get answers from your team or previous buyers. This content is a goldmine for long-tail keywords and can address purchase barriers directly.
Make sure to mark up this content with FAQPage schema. This can help you capture more space in the search results with a rich snippet that answers the questions directly.

5. How to Optimise Category Pages for SEO
Category pages act as hubs for your products. They are often the best pages to target mid-funnel, commercial-intent keywords.
Develop a Strong Category Content Strategy
Write Helpful Category Descriptions
Don’t just show a grid of products. Add a unique, keyword-rich introduction at the top of the page to provide context for both users and search engines.
- Explain what the category contains and who the products are for.
- Naturally include your primary and secondary keywords.
- Link to important subcategories and relevant buying guides.
Example category page intro for “Men’s Trail Running Shoes”:
“Find the perfect pair of men’s trail running shoes for your next off-road adventure. Whether you’re tackling technical singletrack in the Blue Mountains or enjoying a casual run through local parklands, our collection has you covered. We stock everything from minimalist shoes for a natural feel to max-cushion models for ultimate comfort, with options for wide feet and waterproof GORE-TEX protection. Shop top brands like Hoka, Salomon, and Altra with confidence, thanks to our 30-day comfort guarantee.”
Implement a Clear Page Structure
Use headings to structure your category pages logically. This helps with scannability and SEO.
- H1: The main category name (e.g., “Men’s Trail Running Shoes”).
- H2s: Subcategories (e.g., “Max Cushion,” “Waterproof”), featured brands, or a link to a buying guide.
- H3s: Use for specific product callouts or seasonal collections.
Use Internal Linking and Schema to Add Context
Add Category-Specific Schema
Use structured data to help Google understand your category pages. This includes ItemList schema to mark up the list of products shown on the page and BreadcrumbList for navigation.
Link Categories Strategically
Internal linking helps distribute authority and guides users through your site. On category pages, you should link to relevant subcategories and related top-level categories.
You should also link *to* your category pages from relevant blog posts and from your homepage. This signals to Google that they are important hub pages.
6. Core Web Vitals & Performance
Site speed and user experience are major ranking factors. A slow, clunky site will frustrate users and get penalised by Google.
What are the 2025 Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific metrics that Google uses to measure a page’s overall user experience. You can track your performance in Google Search Console.
| Metric | Target | What it Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Under 2.5 seconds | Loading performance (how fast the main content appears). |
| Interaction to Next Paint (INP) | Under 200 milliseconds | Responsiveness (how quickly the page reacts to user input). |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Under 0.1 | Visual stability (how much the page layout shifts during loading). |
How can you improve site performance?
Image Optimisation
Large, unoptimised images are the most common cause of slow e-commerce sites. This should be your first area of focus.
- Use next-gen formats like WebP or AVIF, which offer better compression than JPEG.
- Implement lazy loading so images below the fold only load when a user scrolls to them.
- Serve responsive images that are sized appropriately for the user’s device.
Code Optimisation
Bloated code and too many third-party apps can drag your site down. Regularly audit your code and plugins.
- Minimise render-blocking JavaScript and CSS that slow down initial page load.
- Remove unused code and old app scripts that may still be loading.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Cloudflare or Fastly to serve assets from servers closer to your users.
Mobile Performance
According toStatista, mobile commerce is projected to account for over 60% of all online retail sales in Australia by 2025. A mobile-first approach is no longer optional.
- Use a responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes.
- Ensure buttons and links are large enough to be easily tapped (at least 48×48 pixels).
- Use a minimum font size of 16px for body text to ensure readability without zooming.
7. Structured Data & Schema
Schema markup is a type of code that helps search engines understand the content and context of your pages. This can lead to rich results, making your listings stand out.
What are the essential schema types for e-commerce?
□ Product Schema
This is the most important one. It allows you to display price, availability, and review ratings directly in the search results.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Your Product Name",
"brand": "Your Brand Name",
"sku": "SKU12345",
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"price": "149.99",
"priceCurrency": "AUD",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock",
"url": "https://yourstore.com.au/product-url"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "215"
}
}□ BreadcrumbList & ItemList Schema
As mentioned earlier, BreadcrumbList schema is used for your navigation paths. ItemList schema should be used on category pages to define the collection of products being displayed.
□ Review & Rating Schema
This works with Product schema to show star ratings. You can mark up individual reviews or use AggregateRating for the overall score.
How do you implement and validate schema?
□ Use JSON-LD Format
Google recommends using JSON-LD. It’s implemented as a script in the “ or “ of your HTML and doesn’t interfere with your page’s visible content, making it easier to manage.
□ Validate Your Schema Markup
- Test your pages with Google’s Rich Results Test tool to see which rich results can be generated.
- Use the Schema Markup Validator for more detailed error checking.
- Monitor the Enhancements reports in Google Search Console to find and fix site-wide issues.
8. Google Merchant Center & Feeds
A high-quality product feed is the foundation of any successful Google Shopping campaign. It’s also necessary for free product listings.
Optimise Your Product Feed
How to improve product feed quality
The more detailed and accurate your feed is, the better Google can match your products to relevant searches. You can use feed management tools like DataFeedWatch to optimise and sync your data.
- Include all required attributes like `id`, `title`, `description`, `link`, `image_link`, `availability`, `price`, and `brand`.
- Add optional attributes like `product_type`, `google_product_category`, and `color` to provide more context.
- Use high-quality, professional images with a white background.
- Optimise your product titles with keywords people actually search for, like brand, model, and key features.
Monitor Your Feed Health
Product disapprovals can take your items out of Shopping results entirely. Check the “Diagnostics” section in Merchant Center at least once a week.
- Address any disapprovals or warnings immediately.
- Set up automatic feed updates to keep your inventory and pricing accurate.
- Ensure the data in your feed perfectly matches the data on your product pages.
9. Content Marketing & UGC
Content marketing builds authority, attracts links, and captures customers at the top of the sales funnel. User-generated content (UGC) builds trust at the bottom.
Develop a Content Strategy That Sells
Create Helpful Supporting Content
Think beyond your product pages. What questions does your audience have before they’re ready to buy?
- Buying guides: “The Ultimate Guide to Choosing a Coffee Machine.”
- How-to articles: “How to Set Up and Use Your New Drone.”
- Comparison posts: “iPhone 15 Pro vs. Samsung Galaxy S24.”
- Gift guides: “Top 10 Father’s Day Gifts for the BBQ Enthusiast.”
Build Topic Clusters
This is a powerful strategy where you create a central “pillar” page on a broad topic (often a category page) and surround it with “cluster” content that covers specific subtopics in more detail. All the cluster pages link back to the pillar page, establishing your site as an authority on the topic.
Here is a full guide on how to create a topical map for your site.
Encourage and Showcase User-Generated Content
UGC includes reviews, testimonials, and customer photos. It’s highly trusted by shoppers and provides fresh, unique content for your pages.
- Send post-purchase emails asking for reviews and offering a small incentive.
- Create a branded hashtag and encourage customers to share photos on social media.
- Use a platform like Bazaarvoice to collect and display customer photos and testimonials on your product pages.

10. Technical SEO Essentials
Technical SEO ensures your site can be crawled and indexed efficiently by search engines. A regular technical audit is a must.
How do you manage crawlability and indexation?
Manage Your Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is the number of pages Google will crawl on your site at any given time. For large e-commerce sites, you want to make sure Google spends its time on your most important pages.
- Block low-value pages (like filtered URLs) with your robots.txt file.
- Use the `noindex` tag for thin content pages you want Google to ignore.
- Consolidate duplicate pages using canonical tags.
- Monitor your crawl stats in Google Search Console to identify any issues.
Handle Duplicate Content
Duplicate content happens when the same or similar content appears on multiple URLs. It’s a common issue for online stores due to product variations and faceted navigation.
- Implement self-referencing canonical tags on all your main pages.
- Use canonicals to point product variation URLs (e.g., by colour or size) to a single, main product page.
- Use 301 redirects to permanently move discontinued products to a relevant replacement.
Strengthen Your Internal Linking and URL Management
Create a Smart Internal Linking Strategy
Good internal linking helps search engines understand your site structure and discover your most important pages. A common problem I see with clients is “orphan pages” with no internal links pointing to them.
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to conduct a crawl of your site and find these pages. Then, link to important products and categories from high-authority pages like your homepage or popular blog posts using keyword-rich anchor text.
11. Off-Page SEO & Digital PR
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings. This is primarily about building high-quality backlinks.
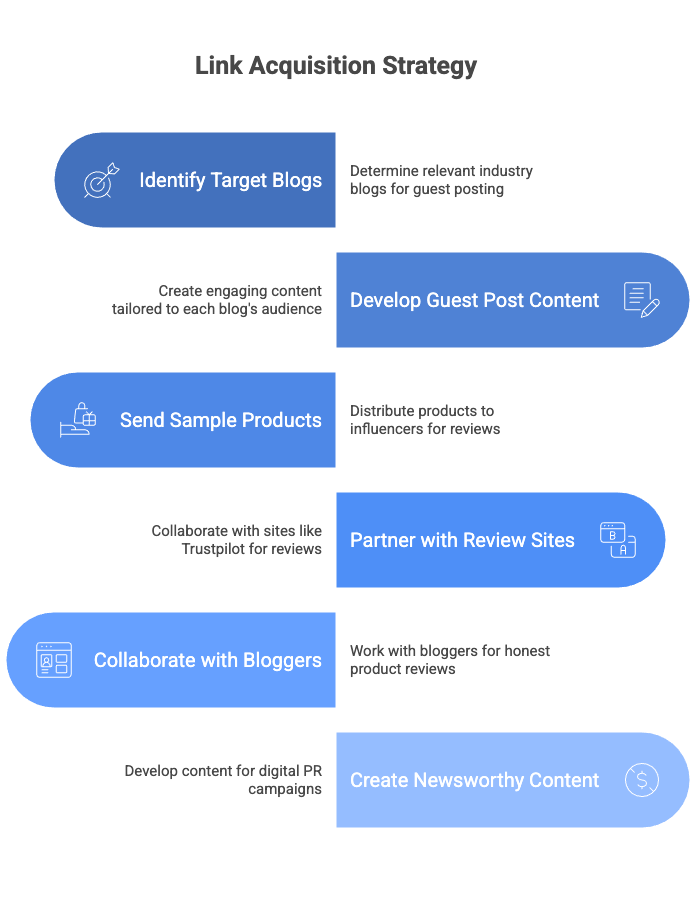
What’s the best way to build links for an e-commerce site?
Develop a Link Acquisition Plan
Focus on earning links from relevant and authoritative websites in your industry. Quality always trumps quantity.
- Write guest posts for popular blogs in your niche.
- Send your products to influencers and bloggers for honest reviews.
- Create newsworthy content, like an industry report or survey, and pitch it to journalists.
- Find “resource pages” that list helpful links and ask to have your site included.
Implement a Brand Mention Strategy
People may mention your brand online without linking to you. These unlinked brand mentions are low-hanging fruit for link building.
Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to set up alerts for your brand name. When you find an unlinked mention, reach out to the site owner and politely ask if they would consider adding a link back to your homepage or a relevant product page.
Optimise for Local Search
Claim and Optimise Your Business Listings
If you have a physical store, local SEO is essential. Start by claiming and fully optimising your Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business).
- Fill out every section of your profile, including services, products, and attributes.
- Ensure your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) are consistent everywhere online.
- Upload high-quality photos of your store and products.
- Encourage customers to leave reviews on Google and respond to them all.

12. Analytics & Performance Tracking
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Setting up proper tracking is the only way to know if your SEO efforts are paying off.
Set Up Essential Tracking Correctly
Configure Google Analytics 4 for E-commerce
GA4 is powerful, but it needs to be configured correctly to track your sales funnel. Make sure you have Enhanced Ecommerce tracking set up.
- Track key events like `view_item`, `add_to_cart`, and `purchase`.
- Create custom reports in the “Explore” section to analyse user paths and behaviour.
- Monitor the performance of individual products and categories.
Monitor Search Console Performance
Regularly check your Search Console reports to stay on top of your site’s health and organic visibility.
- Track your rankings, impressions, and click-through rate for important keywords.
- Monitor your Core Web Vitals scores and address any pages marked as “Needs improvement” or “Poor.”
- Use the “Pages” report to find and fix any indexing issues.
How do you analyse and improve performance?
Conduct Regular Reporting
Set up a monthly SEO report that tracks your key performance indicators (KPIs). This should include organic traffic, conversion rate from organic traffic, keyword ranking improvements, and revenue generated from the organic channel.
Use A/B Testing for Optimisation
A/B testing involves showing two different versions of a page to users to see which one performs better. Use tools like Optimizely or VWO to test changes.
- Test different product page layouts, headlines, and calls-to-action.
- Experiment with your category page designs and filtering options.
- Measure the impact on conversion rate, average order value, and add-to-cart rate.
13. Advanced Strategies
Once you’ve mastered the fundamentals, you can explore more advanced tactics to gain a competitive edge.
Optimise for Voice and AI-Driven Search
How do you optimise for voice search?
Voice searches are typically longer and more conversational. To capture this traffic, you need to think about the questions people ask their smart speakers.
- Target long-tail, conversational keywords in your content.
- Create detailed FAQ pages that answer common customer questions directly.
- Optimise your Google Business Profile for local “near me” searches.
Prepare for AI Overviews
Google’s AI Overviews (formerly SGE) generate direct answers at the top of the search results. To have your content featured, you need to establish strong E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness).
This means creating comprehensive, authoritative content, building a strong backlink profile, showcasing customer reviews, and making it clear who is behind your brand.
Expand with International SEO
What is a multi-market strategy? (if applicable)
If you sell to customers in multiple countries, you need a proper international SEO strategy to show the correct version of your site to the right users.
- Implement `hreflang` tags to tell Google which language and region each page is targeting.
- Use a country-specific domain (like `.co.nz`) or subdirectories (like `/en-au/`).
- Localise your content, including currency, language, and cultural references.
Hreflang implementation example:
<!-- Australian version -->
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-au" href="https://store.com.au/products/shoes" />
<!-- New Zealand version -->
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-nz" href="https://store.co.nz/products/shoes" />
<!-- Default/International version -->
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://store.com/products/shoes" />
Your Ongoing E-Commerce SEO Maintenance Schedule
SEO is not a one-time task. It requires consistent effort to maintain and improve your rankings over time.
| Timeframe | Key Actions | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Weekly | Monitor GMC feed, check GSC for critical errors, track rankings. | Prevent sudden ranking drops and fix issues quickly. |
| Monthly | Analyse keyword performance, update key content, review analytics. | Achieve incremental gains and spot trends. |
| Quarterly | Conduct a full technical audit, analyse competitors, plan content. | Identify new growth opportunities and stay ahead. |
| Annually | Review your overall SEO strategy, plan major site updates. | Align SEO with long-term business goals. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does e-commerce SEO take to show results?
You can typically see initial improvements from technical fixes within 1-3 months. However, significant results from content and authority-building efforts usually take 6-12 months of consistent work.
What’s the most important ranking factor for e-commerce sites?
There isn’t one single “most important” factor. It’s a combination of technical health (especially Core Web Vitals), high-quality product and category pages, and strong site authority built through backlinks and positive user signals.
How do I handle out-of-stock products for SEO?
For temporarily out-of-stock items, keep the page live and offer a “notify me when back in stock” option. For permanently discontinued products with no direct replacement, use a 410 “Gone” status code. If there’s a good alternative, use a 301 redirect to the new product page.
Is Shopify good for SEO?
Yes, Shopify is a strong platform for SEO. It handles many technical basics out of the box, but you still need to optimise it. Key areas to focus on are editing the robots.txt file, managing collections for faceted navigation, and creating unique content.
How is e-commerce SEO different from regular SEO?
E-commerce SEO has a greater focus on site architecture due to the large number of pages. It also involves optimising for transactional keywords, managing faceted navigation, implementing detailed product schema, and integrating with platforms like Google Merchant Center.
What’s the difference between SEO and SEM for e-commerce?
SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) focuses on earning unpaid, organic traffic from search engines. SEM (Search Engine Marketing) is a broader term that includes SEO but also paid advertising, such as Google Shopping Ads and text ads.
A strong e-commerce strategy uses both. SEO builds long-term, sustainable traffic, while SEM can drive immediate sales and provide valuable keyword data.